Intro
A massive leak of internal Google Search ranking documentation has sent shockwaves through the SEO community. The leak, which exposed over 14,000 potential ranking features, offers an unprecedented look under the hood of Google’s closely guarded search rankings system.
The Story Behind the Leak
Erfan Azimi shared a Google API document leak with SparkToro’s Rand Fishkin, who then enlisted Michael King of iPullRank to help disseminate the information. The leaked files, originating from a Google API document commit titled “yoshi-code-bot /elixer-google-api,” were not the result of a hack or a whistleblower, but rather an internal document release.
Overview of the Leak
The leak provides a comprehensive view of Google’s ranking factors, revealing insights into PageRank variations, site authority metrics, and much more. Here’s a detailed breakdown:
Key Insights from the Google Search Document Leak
PageRank and Its Variations
-
PageRank_NS: Now deprecated, this algorithm is associated with document understanding and modifies the traditional PageRank to focus on a localized subset of the network around seed nodes.
-
Seven Types of PageRank: Google mentions seven different types of PageRank, including the famous ToolBarPageRank. These variations indicate that Google employs multiple methods to assess page importance.
Business Model Identification
Google’s algorithm can identify various business models, including news sites, YMYL (Your Money or Your Life) sites, personal blogs, ecommerce, and video sites. The reason behind specifically filtering for personal blogs remains unclear and raises questions about Google's broader intentions.
Algorithm Components
-
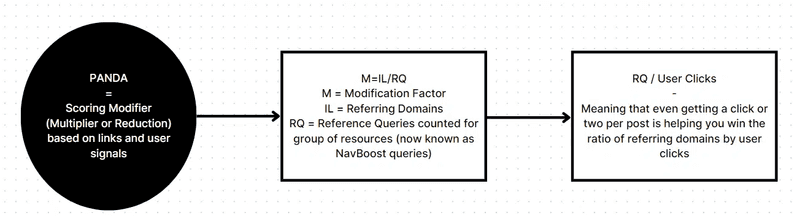
NavBoost: A re-ranking mechanism based on user behavior and click logs, heavily influenced by Chrome data.
-
NSR (Normalized Site Rank): Used to compute site rank for host-level site chunks.
-
ChardScores: Site-level scores predicting site/page quality based on content.
Site Authority Metrics
Google uses a site-wide authority metric and several signals, including traffic from Chrome browsers, to evaluate site authority. This suggests that overall site quality and credibility play significant roles in ranking.
Embedding Techniques and Topical Authority
-
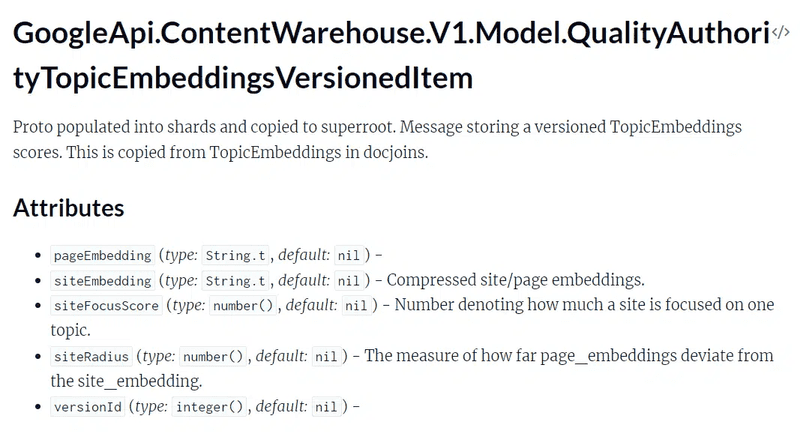
Page and Site Embeddings: Google employs page embeddings, site embeddings, site focus, and site radius in its scoring function to understand the topical relevance and consistency of a website’s content.
-
Topic Borders and Topic Authority: Metrics like siteFocusScore, siteRadius, siteEmbeddings, and pageEmbeddings are used to measure topical authority, emphasizing the importance of maintaining a clear topical focus.
Click Data and User Engagement
-
NavBoost: NavBoost relies on click data and user behavior to re-rank search results, underscoring the importance of user engagement metrics.
-
Click Metrics: Google measures various types of clicks, including bad clicks, good clicks, last longest clicks, and site-wide impressions.
Quality NSR Data Insights
Key scoring factors from the NSR data document include:
-
titlematchScore: A sitewide title match score indicating how well titles match user queries.
-
site2vecEmbedding: A sitewide vector similar to word2vec, highlighting the importance of comprehensive site embeddings.
-
pnavClicks: Likely related to navigational information derived from user click data.
-
chromeInTotal: Site-wide Chrome views, emphasizing the importance of site-wide signals.
-
chardVariance and chardScoreVariance: Scores predicting site/page quality based on content, with consistency being key.
Practical Takeaways for SEO Professionals
-
Invest in a Well-Designed Site: Ensure your site has intuitive architecture to optimize for NavBoost, which relies on user behavior and click logs for re-ranking search results.
-
Remove/Block Topically Irrelevant Pages: Remove or block pages that aren't topically relevant. Establish your target topic and ensure each page scores well in this area.
-
Optimize Headings and Content: Optimize headings around queries and ensure paragraphs clearly answer those queries to improve page embeddings and relevance.
-
Focus on Clicks and Impressions: Write content that attracts more impressions and clicks, emphasizing user engagement.
-
Regularly Update Content: Regularly update content with unique information, new images, and videos to maintain freshness and score high on effort calculations.
-
Maintain High-Quality Content: Consistency in high-quality content is crucial. Google’s site-level chard scores predict site/page quality based on content.
-
Value Impression Growth: Growing impressions is a positive sign of site performance.
-
Optimize for Entity Salience: Focus on improving salience scores for entities and top entity identification as mentioned in the leak.
-
Remove Poorly Performing Pages: Identify and eliminate pages with poor user metrics and no backlinks to maintain high site-wide scores.
How to Remove Google’s Memory of an Old Version of a Document
According to the leak, Google keeps a record of every version of a webpage, maintaining an internal web archive similar to the Wayback Machine. However, Google only uses the last 20 versions of a document. If you update a page, wait for a crawl, and repeat the process 20 times, you can effectively push out certain versions of the page. This tactic could be useful for improving historical weights and scores associated with older versions.
Google Search Ranking System
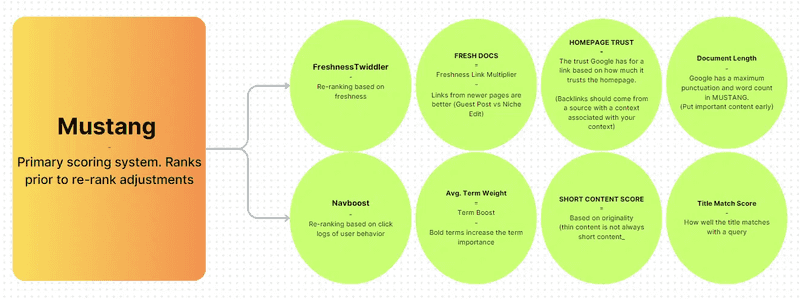
One interesting conjecture from the leak is the impact of term weight (literal size). Bolding words or adjusting the size of words may influence document scores. Additionally, Google’s index storage mechanisms prioritize content differently:
-
Flash Drives: For the most important and regularly updated content.
-
Solid State Drives: For less important content.
-
Standard Hard Drives: For irregularly updated content.
Google’s Indexer: Alexandria
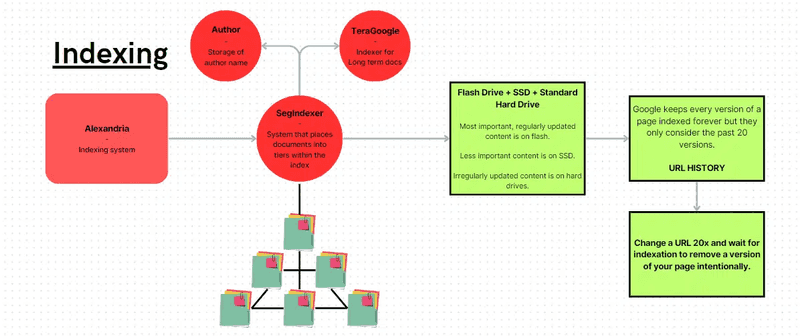
Google’s indexer is named Alexandria, after the famous library. Other indexers mentioned include SegIndexer, which places documents into tiers, and TeraGoogle, which handles long-term memory storage.
Seed Sites and Sitewide Authority
The leak mentions a factor named isElectionAuthority, possibly indicating seed sites or topical authorities. It suggests that sites with high authority, such as those with a PageRank of 9/10, have significant influence. However, nsrIsElectionAuthority is considered deprecated, leaving some ambiguity in interpretation.
Short Content Can Rank
Contrary to common belief, short content does not equal thin content. The leak confirms that short content can rank well, albeit with a different scoring system.
Fresh Links vs. Existing Links
According to the freshdocs link value multiplier, links from newer webpages are more valuable than those inserted into older content. This indicates that while niche edits can be effective, fresh links have a higher impact.
Favorite Discoveries
Page Quality (PQ)
Google uses an LLM to estimate “effort” for article pages, helping determine whether a page can be easily replicated. Tools, images, videos, unique information, and depth of information are ways to score high on effort calculations.
Topic Borders and Topic Authority
Topical authority, supported by siteFocusScore, siteRadius, siteEmbeddings, and pageEmbeddings, is crucial. Maintaining a clear topical focus and minimizing deviation from the topic helps improve rankings.
Image Quality
ImageQualityClickSignals measures image quality based on click data (usefulness, presentation, appealingness, engagingness).
Host NSR
Host NSR is site rank computed for host-level site chunks, measuring quality in segments. This chunking system helps Google assess site quality comprehensively.
Unified Theory of Ranking
This section attempts to consolidate the factors from the leak into a mathematical formula, highlighting various metrics and their impacts on the overall ranking score (R).
Definitions and Metrics
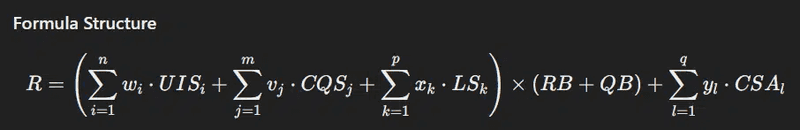
User Interaction Scores (UIS):

-
UgcScore: User-generated content engagement.
-
TitleMatchScore: Relevance of titles to user queries.
-
ChromeInTotal: Total interactions tracked via Chrome.
-
SiteImpressions: Total site impressions.
-
TopicImpressions: Impressions on topic-specific pages.
-
SiteClicks: Click-through rate for the site.
-
TopicClicks: Click-through rate for topic-specific pages.
Content Quality Scores (CQS):
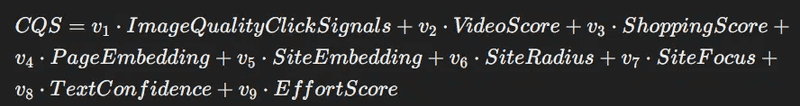
-
ImageQualityClickSignals: Quality signals from image clicks.
-
VideoScore: Quality and engagement of video content.
-
ShoppingScore: Score for shopping-related content.
-
PageEmbedding: Semantic embedding of page content.
-
SiteEmbedding: Semantic embedding of site content.
-
SiteRadius: Deviation measure within the site embedding.
-
SiteFocus: Metric indicating topic focus.
-
TextConfidence: Confidence in the text’s relevance and quality.
-
EffortScore: Effort and quality in content creation.
Link Scores (LS):
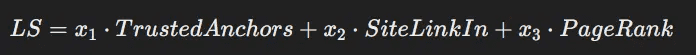
-
TrustedAnchors: Quality and trustworthiness of inbound links.
-
SiteLinkIn: Average value of incoming links.
-
PageRank: Various PageRank scores (0, 1, 2, ToolBar, NR).
Relevance Boost (RB):

-
TopicEmbedding: Relevance over time.
-
QnA: Baseline quality measure.
-
STS: Aggregate score based on text understanding, salience, and entities.
Quality Boost (QB):
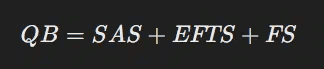
-
SAS: Site authority score relating to trust, reliability, and link authority.
-
EFTS: Effort score incorporating text, multimedia, and comments.
-
FS: Freshness score based on update and original post dates.
-
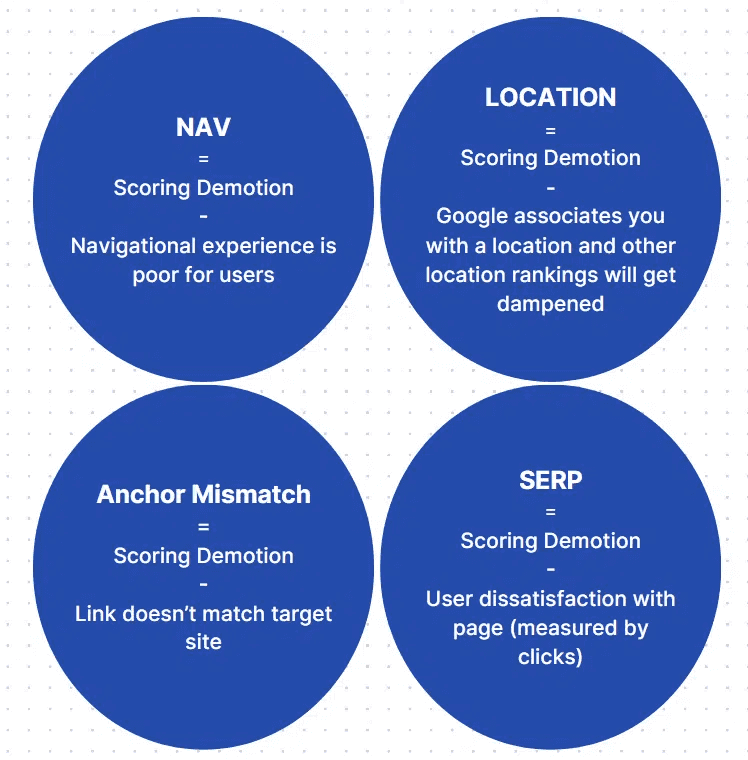
CSA: Content-specific adjustments based on SERP and on-page features.
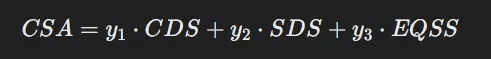
Content-Specific Adjustments (CSA):
-
CDS: Chrome data score focusing on impressions and clicks across the site.
-
SDS: Serp demotion score based on SERP experience measurement.
-
EQSS: Experimental Q Star score for experimental variables.
Full Formula
R=(∑i=17wi⋅UISi)+(∑i=19vi⋅CQSi)+(∑i=13xi⋅LSi)×(RB+QB+X)−
R=((w1⋅UgcScore+w2⋅TitleMatchScore+w3⋅ChromeInTotal+w4⋅SiteImpressions+w5⋅TopicImpressions+w6⋅SiteClicks+w7⋅TopicClicks)+(v1⋅ImageQualityClickSignals+v2⋅VideoScore+v3⋅ShoppingScore+v4⋅PageEmbedding+v5⋅SiteEmbedding+v6⋅SiteRadius+v7⋅SiteFocus+v8⋅TextConfidence+v9⋅EffortScore)+(x1⋅TrustedAnchors+x2⋅SiteLinkIn+x3⋅PageRank))×(TopicEmbedding+QnA+STS+SAS+EFTS+FS)+(y1⋅CDS+y2⋅SDS+y3⋅EQSS)
Generalized Scoring Overview
1. User Engagement:
- UgcScore, TitleMatchScore, ChromeInTotal, SiteImpressions, Topic Impressions, Site Clicks, Topic Clicks
2. Multi-Media Scores:
- ImageQualityClickSignals, VideoScore, ShoppingScore
3. Links:
- TrustedAnchors, SiteLinkIn (average value of incoming links), PageRank (0, 1, 2, ToolBar, NR)
4. Content Understanding:
- PageEmbedding, SiteEmbedding, SiteRadius, SiteFocus, TextConfidence, EffortScore
Conclusion
The documentation leak provides invaluable insights into Google’s ranking mechanisms, debunking several myths and revealing intricate factors influencing search results. SEO professionals can leverage this knowledge to refine their strategies, focusing on user engagement, topical relevance, and consistent content quality. As the SEO community digests these revelations, many will likely reconsider their approaches in light of this new information.
By understanding and applying these insights, SEO practitioners can better navigate the complexities of Google's ranking system, ultimately enhancing their website's visibility and performance in search results.

